
Inter-relationships of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter mechanisms and clinical implications. Risk of atrial fibrillation, stroke, and death after radiofrequency catheter ablation of typical atrial flutter. Seara JG, Roubin SR, Gude Sampedro F, Barreiro VB, Sande JM, Mañero MR, et al. Prophylactic pulmonary vein isolation during isthmus ablation for atrial flutter: the PReVENT AF Study I. Steinberg JS, Romanov A, Musat D, Preminger M, Bayramova S, Artyomenko S, et al. Results from a single-blind, randomized study comparing the impact of different ablation approaches on long-term procedure outcome in coexistent atrial fibrillation and flutter (APPROVAL). Mohanty S, Mohanty P, di Biase L, Bai R, Santangeli P, Casella M, et al. Prophylactic pulmonary vein isolation during cavotricuspid isthmus ablation for atrial flutter: a meta-analysis.
Koerber SM, Turagam MK, Gautam S, Winterfield J, Wharton JM, Lakkireddy D, et al.
#CTI ABLATION FLUTTER TRIAL#
Prophylactic atrial fibrillation ablation in atrial flutter patients without atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Pulmonary vein triggers play an important role in the initiation of atrial flutter: initial results from the prospective randomized Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Atrial Flutter (Triple A) trial. Schneider R, Lauschke J, Tischer T, Schneider C, Voss W, Moehlenkamp F, et al. Prophylactic pulmonary vein isolation during isthmus ablation for atrial flutter: three-year outcomes of the PREVENT AF I study. Romanov A, Pokushalov E, Bayramova S, Ponomarev D, Shabanov V, Losik D, et al. Pulmonary vein isolation to reduce future risk of atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing typical flutter ablation: results from a randomized pilot study (REDUCE AF). Ablation of atrial fibrillation at the time of cavotricuspid isthmus ablation in patients with atrial flutter without documented atrial fibrillation derives a better long-term benefit. Navarrete A, Conte F, Moran M, Ali I, Milikan N. Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation ablation – sequential or combined? A cost-benefit and risk analysis of primary prevention pulmonary vein ablation. Gula LJ, Skanes AC, Klein GJ, Jenkyn KB, Redfearn DP, Manlucu J, et al. Incidence and predictive factors of atrial fibrillation after ablation of typical atrial flutter. Laurent V, Fauchier L, Pierre B, Grimard C, Babuty D. Incidence of atrial fibrillation post-cavotricuspid isthmus ablation in patients with typical atrial flutter: left-atrial size as an independent predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence. 2004 90(1):59–63.Įllis K, Wazni O, Marrouche N, Martin D, Gillinov M, McCarthy P, et al. Long term follow up of radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial flutter: clinical course and predictors of atrial fibrillation occurrence. 2002 106(6):649–52.īertaglia E, Zoppo F, Bonso A, Proclemer A, Verlato R, Corò L, et al. Contemporary management of atrial flutter. Large prospective RCTs are warranted to confirm the benefit of prophylactic PVI in typical AFL. Our study indicated the efficacy and safety of prophylactic PVI during CTI ablation in typical AFL patients without AF history, especially for elder patients. There is a lower occurrence of AF in prophylactic PVI group (27% versus 46%, OR = 0.45, 95% CI: 0.28 to 0.73 P = 0.001) and no difference of complications between prophylactic PVI group and CTI group (4% versus 2% P = 0.33).
In the subgroup of age > 55, prophylactic PVI showed even higher incidence of freedom from AA.
#CTI ABLATION FLUTTER FREE#
More patients in prophylactic PVI group were free from atrial arrhythmias (AA) compared with those in CTI group (69% versus 50%, OR = 2.36, 95% CI: 1.51 to 3.68 P = 0.0001). A total of 357 patients with follow-up of 20 ± 9 months were included. Resultsįour RCTs met the inclusion criteria. Randomized controlled trials (RCT) comparing prophylactic PVI to CTI ablation alone in typical AFL patients without prior documentation of AF were identified in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases. The meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the benefit of prophylactic pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) in typical AFL patients.
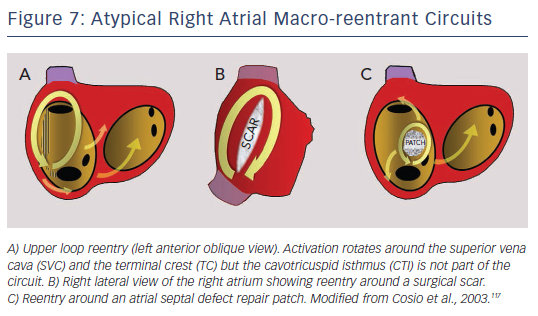
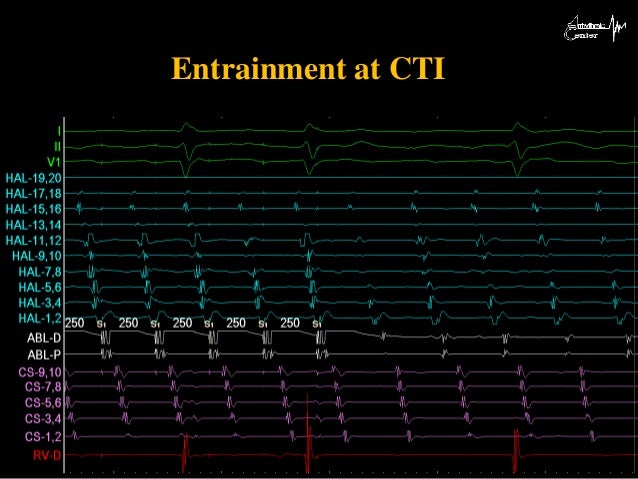
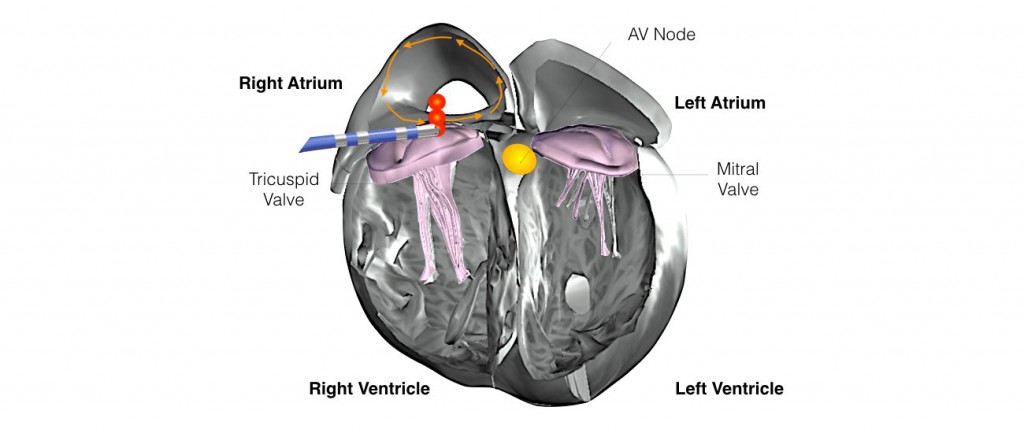
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is common after cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI)–dependent atrial flutter (AFL) ablation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
